Qualitative analysis of Organic compounds (Part 2)
As mentioned in the previous post, preliminary tests act as a base of qualitative analysis. In this step, the physical characteristics of the organic compounds are observed.The various tests are,
Colour
Small organic compounds are usually colourless. The colour in organic compound is due to the presence of a group called a chromophore.This group plays an essential part when we study the Ultra- violet spectra of organic compounds.
Odour
Certain functional groups show a characteristic odour. This can help us gauge the type of functional group present in the organic compound. For example, esters give off a fruity odour.
State
Compounds can be either solid or liquid.
When the compound looks like talcum powder, it is an amorphous solid. Whereas, when the crystals are defined, it is considered crystalline.
 |
| Crystalline |
 |
| Amorphous |
The basic difference between the two is the molecular arrangement. When the molecules are arranged in a proper order it is a crystalline solid. Whereas, when there is no order in the molecular arrangement, it is an amorphous solid.
Ignition Test
This test lets us know if a particular compound is aromatic or aliphatic. Aromatic compounds when exposed to direct flame give off soot whereas aliphatic compounds do not give off soot.
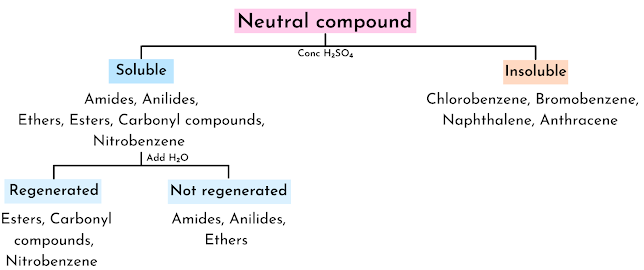
Solubility
In the qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds, solubility is helpful for the identification of cations. Similarly, solubility is a very important test that helps in the identification of a functional group. Like cations, functional groups are classified based on their solubility as
- Strong acid
- Weak acid
- Base
- Neutrals
- Polynuclear aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons
- Miscellaneous




Comments
Post a Comment