Configuration of Geometric Isomers (E/Z and Cis/Trans)
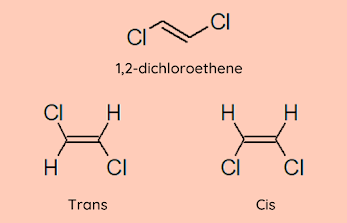
Geometric isomers are formed when the rotation of the Carbon-Carbon bond is restricted either due to a double bond or the carbon-carbon single bond is a part of a chain. Cis and Trans This notation is used when both carbons have the same substituent. If the substituents are on the same side, then the isomer is cis else it is trans. The physical properties of cis and trans isomers vary. Polarity Symmetrical Boiling Point Melting Point Cis Alkenes More Less Higher Lower Trans Alkenes Less More Lower Higher In an acyclic molecule,usually, the stability of a trans isomer is higher than a cis isomer because of steric hindrance between the substituents in the cis isomers. When the carbons have different substituents, cis/trans nomenclature cannot be used. Here, E/Z is used. E/Z First we need to understand how to assign priority to the substituents to denote the E/Z configuration. The priority is denoted...

