Isomerism in Organic Compounds- I
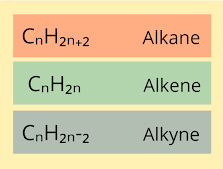
Isomers are sets of molecules which possess the same molecular formula but have a different arrangement of the atoms in space. This is the definition you might have read. Let us take an example. Think about the formula of C₆H₁₂. What would its structure be? Since it follows the CₙH₂ₙ, we know that it probably is an alkene. An alkene is a hydrocarbon that possesses a double bond. But the location of the double bond can be identified only based on its IUPAC name. It can have the following possible structures. Or it can even be a cyclic compound. As you can see, each and every compound above has the same molecular formula but the arrangement of atoms in each case is different. Each of these compounds have a different IUPAC name. So, they are all isomers. C₆H₁₂. can have up to 25 isomers. There exist different types of isomers which I will write about in the next post.
