Qualitative analysis of Organic compounds (Part 1)
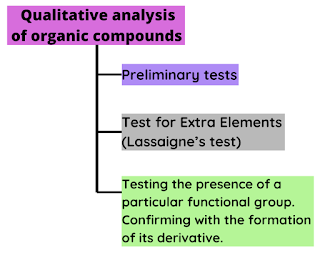
The analysis and identification of organic compounds in a lab is Qualitative analysis of organic compounds. An organic compound usually consists of Carbon, Hydrogen. These compounds may also contain oxygen, halogens, nitrogen, sulphur based on the functional group present. We can divide the qualitative analysis into, Preliminary tests As the name suggests, these tests act as a base of the analysis. The preliminary tests consist of observing various physical characteristics such as color, odour, state, solubility and the ignition test. These tests help determine the steps to be followed. Test for Extra Elements Organic compounds contain other elements such as Halogens, Nitrogen, Sulphur, Oxygen. All the elements mentioned, except Oxygen , are determined by Lassaigne's test. Testing the presence of a functional group and confirming it with the synthesis of its derivative. This steps involves testing the presence of a functional group and then confirmed by the synthesis of its deri...
